PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Published by ELEXAN Scientific on Mar 21st 2025
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance engineering plastic with exceptional mechanical properties, dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and thermal properties. While certain wet chemistries enable the surface functionalization of PEEK¹, its inertness and mechanical strength make it an ideal material for tubing and connectors used in bio and microfluidic applications. PEEK has a relatively high surface energy compared to fluoropolymers like PTFE or FEP, making it non-ideal for applications like transferring nanoparticles.
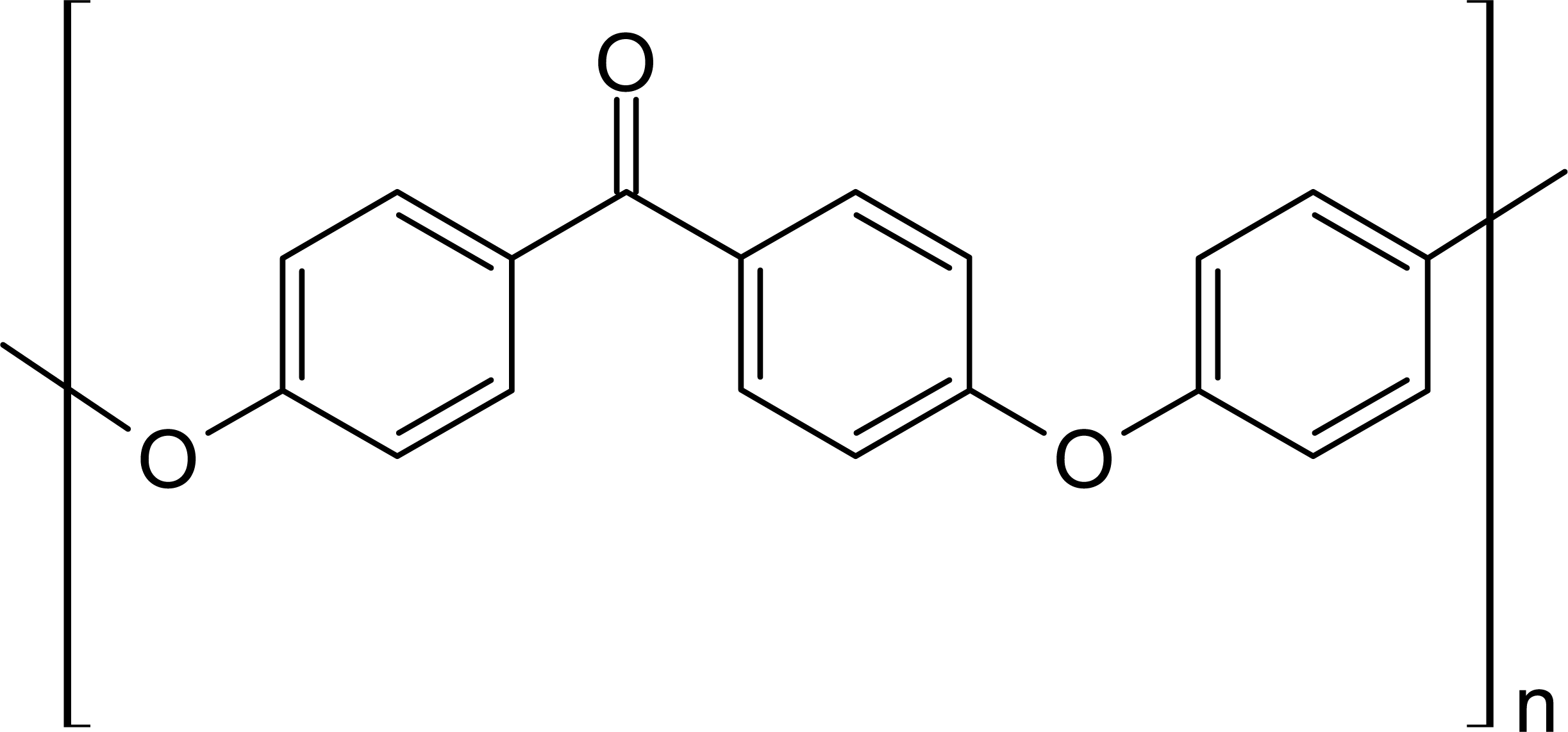 Figure 1. PEEK chemical structure
Figure 1. PEEK chemical structure
PEEK is generally considered incompatible with the following chemicals.
Incompatible Chemicals:
- Methylene Chloride
- THF
- DMSO
- Nitric Acid
- Sulfuric Acid
- Hydrofluoric Acid
- Hydrobromic Acid
- Hydroiodic Acid
- Halogenated gases
PEEK has low permeability, preventing gases and liquids from passing through its structure. This characteristic makes it well-suited for applications that demand high chemical and temperature resistance, as well as long-term durability. Additionally, PEEK offers high dimensional stability under high pressure and temperature, making it suitable for use in high-pressure systems such as HPLC units.
PEEK polymer is produced by different manufacturers in crystalline and amorphous grades and parts are manufactured using virgin (unfilled) or filled polymer. The following table provides PEEK properties across all different brands. For exact values, refer to the specific brand's datasheet. Common PEEK brand names include:
- Ketron®
- SustaPEEK
- TECAPEEK®
- PEEK-LSG
- Semitron® ESd 480
- Susta® PEEK
- Unitrex
- Victrex® PEEK
- Vestakeep PEEK
Note: "-" is used to show the range of properties across different manufacturers, and "/" is used to show the values under different conditions.
| Physical Property | Condition | ASTM | Unit | Value |
| Relative Density | - | D792 | - | 1.26 - 1.32 |
| Mold Shrinkage | - | D955 | % | 1.0 - 1.8 |
| Water Absorption | 24 hrs at 23 °C | D570 | % | 0.1 - 0.5 |
| pH Range | - | - | - | 0 - 14 |
| Thread Strength | - | - | - | Excellent |
| Melt Flow Index | 400 °C/2.16 kg | D1238 | g/10 min | 4 |
| Permeability (Water) | 25 °C | - | ×10 -13 cm³·cm/cm².s·Pa | 160 - 300 |
| Permeability (Oxygen) | 25 °C | - | ×10 -13 cm³·cm/cm².s·Pa | 0.06 - 0.1 |
| Friction Coefficient | Dynamic | D3702 | - | 0.23 - 0.45 |
| Surface Energy (Treated) | - | D2578 | ×10 -3 N/m | 34 - 38 (60) |
| Mechanical Property | Condition | ASTM | Unit | Value |
| Tensile Strength (Yield) | 23 / 250 °C | D638 | MPa | 90 / 12 |
| Tensile Strength (Break) | - | D638 | MPa | 90 - 150 |
| Young's Modulus | - | D638 | GPa | 3.6 - 3.9 |
| Elongation (Yield) | - | D638 | % | 4.9 - 5 |
| Elongation (Break) | - | D638 | % | 30 - 150 |
| Flextural Modulus | 23 / 120 / 250 °C | D790 | GPa | 4.1 / 4.0 / 0.3 |
| Flextural Strength | 23 / 120 / 250 °C | D790 | MPa | 170 / 100 / 12.4 |
| Izod Strength | 23 °C | D256 | J/m | 80 - 94 |
| Hardness (Shore D) | - | D2240 | - | 85 - 95 |
| Electrical Property | Condition | ASTM | Unit | Value |
| Arc Resistance | - | D495 | s | 40 |
| Dielectric Constant | 1 MHz | D257 | - | 3.2 - 3.3 |
| Dielectric Strength | 50 um / 2 mm Thick | D149 | KV/mm | 19 / 20 |
| Dissipation Factor | 1 MHz | D150 | ×10 -4 | 30 |
| Volume Resistivity | - | D257 | ×10 15 omh.cm | 16 - 17 |
| Surface Resistivity | - | D257 | ×10 15 ohm | 10 |
| Thermal Property | Condition | ASTM | Unit | Value |
| Melting Point | - | D3418 | °C | 340 |
| Glass Transition Temp. (T g) | - | DSC | °C | 140 - 145 |
| Ductile Transition Temp. | - | - | °C | -65 - -60 |
| Coeff. of Linear Thermal Exp. | Tg | D696 | ×10 -5 /°C | 4.7 / 10.8 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 23 °C | E1530 | W/m.K | 0.25 |
| Heat Deflection Temp. | 1.8 MPa | D648 | °C | 150 - 160 |
| Max. Cont. Service Temp. | - | - | °C | 154 - 260 |
| Min. Cont. Service Temp. | - | - | °C | -65 - -70 |
| UL Cont. Service Temp. | Mech. / Electr. | °C | 240 / 260 | |
| Fire Resistance | LOI | % | 24 - 35 | |
| Flammability Rating | - | UL94 | - | V0 |
| Sterilization | Condition | ASTM | Unit | Value |
| UV Light Resistance | - | - | - | Good |
| Autoclavable | - | - | - | Yes |
| Steam Sterilization | 200 Cycles | - | - | No Effect |
| Heat Sterilization | up to 260 °C | - | - | No Effect |
| Chemical Sterilization | Ethylene Oxide | - | - | No Effect |
| Gamma Sterilization | 1000 Mrads | - | - | No Effect |
References:
1. Zimmerer, Cordelia, et al. "Surface functionalization of poly (ether ether ketone) by wet-chemical modification with carboxylic acids and diamine." Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 38.1 (2024): 139-162.

